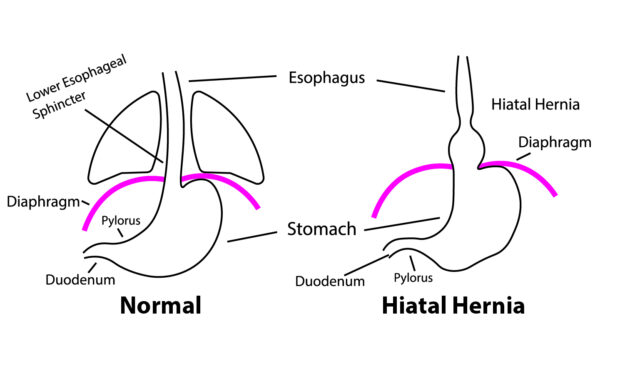
Hiatal hernia
A hiatal hernia occurs when a portion of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. Hiatal hernia is an internal hernia that is not visible externally. Up to 50% of adults have hiatal hernias by the time they turn 60. Some people with hiatal hernia do not experience any symptoms but others can have significant acid reflux. Large hiatal hernias, known as paraesophageal hernias, can cause difficulty swallowing food, chest pain and other symptoms.
Hiatal hernia: What you need to know
- Hiatal hernia can develop at any age, though it most often occurs in people over 50.
- It is associated with obesity, smoking and pregnancy.
- Symptoms are similar to those of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) including heartburn, regurgitation, belching or nausea.
- Tests to help your physician diagnose hiatal hernia may include an endoscopy, barium swallow exam or a CT scan.
Hiatal hernia: Treatments
If you have been diagnosed with hiatal hernia, your treatment options include medication, lifestyle changes or surgery depending on the severity of symptoms.
Lifestyle changes
A common management for hiatal hernia includes lifestyle changes. This can include weight loss, avoiding large meals at night and eating smaller meals more frequently, avoiding caffeine and spicy foods that trigger acid reflux symptoms. Your doctor may also suggest that you avoid lying down or going to bed immediately after eating.
Medication
One of the most common treatment options for hiatal hernia are medications that can help reduce the amount of acid produced in the stomach and therefore symptoms like heartburn and acid reflux. Most commonly prescribed medications include proton-pump inhibitors (e.g., Prilosec, Prevacid, Nexium).
Surgery
Surgery is usually recommended if you experience severe or persistent symptoms that do not respond to or only partially respond to medications. The most common type of surgery for hiatal hernia is a fundoplication. Our surgeons at the UF Health Reflux Center in Jacksonville specialize in this and other operations for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Surgery is performed laparoscopically or robotically with small incisions and involves reducing the stomach back into the abdominal cavity and wrapping the top portion of the stomach around the esophagus to stop GERD. In this way, our surgeons can repair the hernia with less pain and shorter recovery times for you. Recovery from hiatal hernia surgery can vary depending on the individual patient, hernia size and the specific procedure performed, but typically requires one to two nights in the hospital and some dietary modifications.
Hiatal hernia: Our expertise
Many specialists, one goal
You receive coordinated, compassionate care from a number of specialists as well as capable highly trained support staff, all focused on your wellness. Our team works to create an integrated treatment plan that will provide you with the best possible outcomes.
Advanced technologies and facilities
As a part of the region’s leading academic health center, our specialists have access to the most advanced technologies and facilities available. They will incorporate these options into an individualized plan tailored to your needs.
Research-based care
Our physicians, as faculty of the University of Florida, are committed to research and finding the most advanced approaches to patient care. They also participate in numerous national and international clinical trials and offer multiple accredited physician training programs.